Explaining the Meaning of a Swap on Forex: Examples of Use

6 minutes for reading
In this article, we will discuss the use of swap on Forex. Swaps can influence the dynamics of currency pairs significantly and form long-term trends on the market.
What is a swap and how it works?
A swap on Forex is an operation of money depositing or withdrawal for moving an open position to the next day. On Forex, a marginal system of trading is used, which allows using loaned money in the form of large leverage. Thus, when a position is moved to the next day, the rules of interbank crediting come into force.
Swaps on Forex directly depend on the interest rates of Central banks for each currency. In might be said that the currency in the pair that is bought is deposited while the currency that is sold is loaned. The bigger the difference between the rates of the currencies in the pair - the bigger the swap. Depending on whether we are buying or selling a currency pair, a swap will be deposited on or withdrawn from our account:
- A positive swap is a swap that is deposited on the trader's account for each transfer of an open position. It emerges from buying a currency with a high interest rate against a currency with a low rate. For example, for selling USD/MXN, a positive swap will be deposited on your account. We sell the dollar with a low rate (of 0.25%) and buy the Mexican peso with a high rate (of 6.5%).
- A negative swap is a swap withdrawn from the trader's account for each transfer of an open position. It emerges from buying a currency with a low interest rate against one with a high interest rate. For example, for buying USD/ZAR, a negative swap will be withdrawn daily. We buy the dollar with a low rate (of 0.25%) and sell the African (RSA) rand with a high rate (of 5.25%).
The size of swaps depends on the difference between the rates of the currencies and the conditions on which your broker works with crediting organizations. Thus, the size of swaps for the same pairs may differ significantly depending on the broker. In the case of currency pairs having more or less equal interest rates, both the swaps for buys and sells may be negative.
The swap for a currency pair is deposited/withdrawn every day (normally, at midnight server time). There is one peculiarity: Wednesday night, the swap is tripled, while Friday night, when the position is transferred to Monday, the swap remains single. This is since the position opened on Wednesday the valuation date (the date when the trade conditions are fulfilled) is Friday.
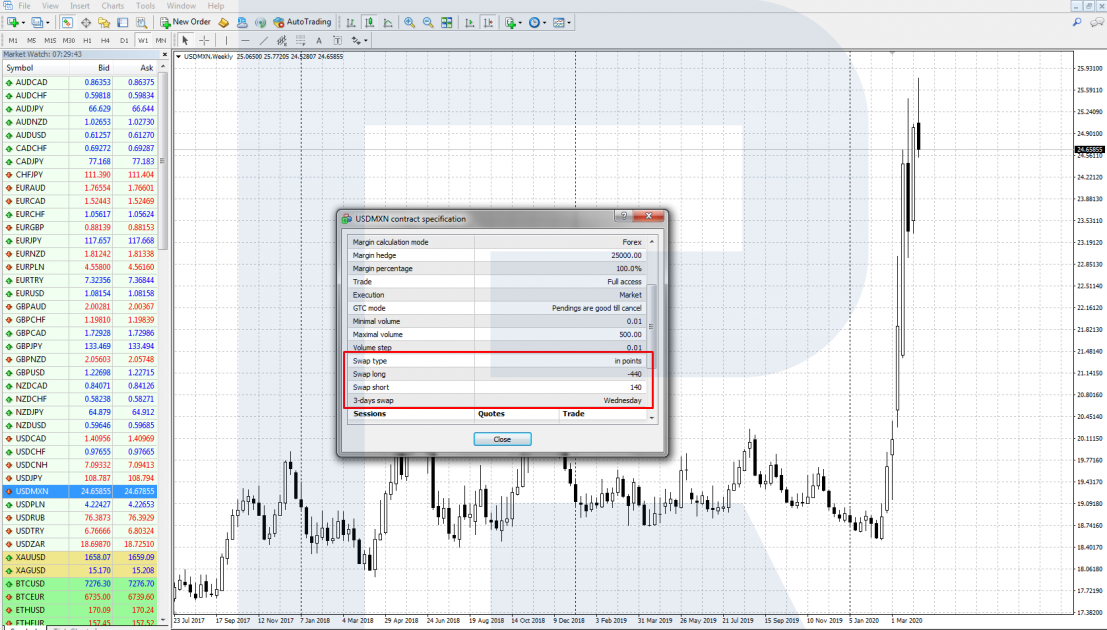
If you plan to hold your position for a rather long time, it will be wise to evaluate the influence of swaps on your position. Study the information on the website of your broker company carefully. In a popular trading terminal MetaTrader 4, to see the size of swaps, right-click the currency pair in the MarketReview window and choose the menu line "Contract specification".
How to make money on swaps?
Thanks to the difference between the interest rates, swaps allow receiving extra profit and can even form long-term trends on the market. The strategy based on using positive swaps is called Carry trade. The idea of the strategy is in holding positions with a positive swap for as long as possible.
To get maximal swaps, we choose a currency pair with a large difference between the interest rates of the currencies it contains. Buying the currency with a high interest rate against the one with a low interest rate, you can every day receive a good positive swap for holding this position.
Carry trade works well when things go smoothly on the market, stock indices grow stably. Investors have no reason for worrying, so the enjoy the opportunity to make money investing in the high-yielding currencies of developing markets. Investing in profitable currencies may form a long-term market trend.
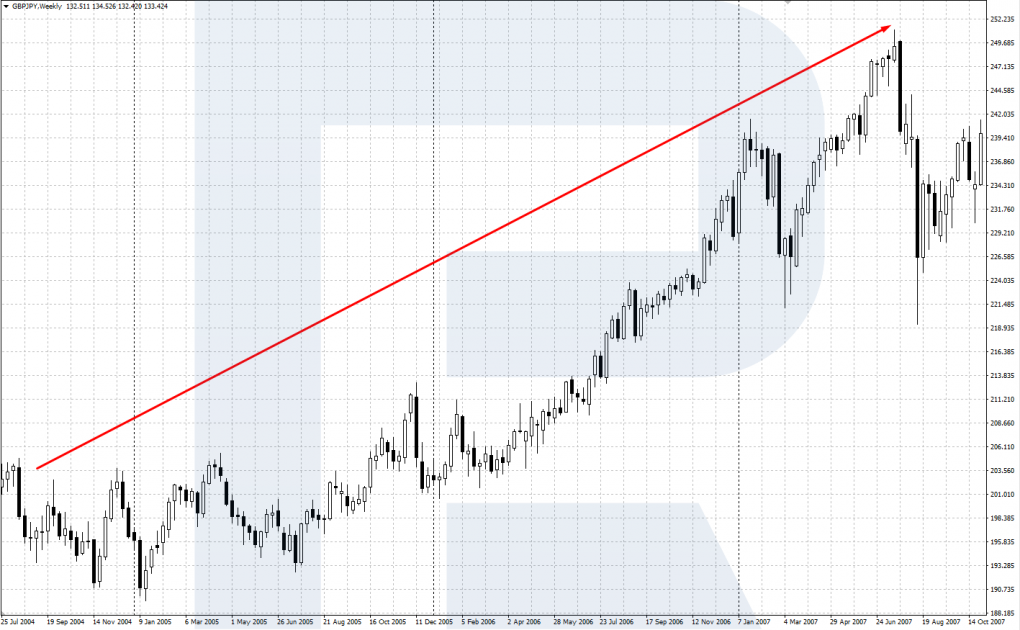
There was a time (before the crisis of 2008) when it was popular to buy GBP/JPY as an instrument of carry trade. The British pound is one of the leading world currencies and had quite a high interest rate of 5.0% at that time. The Japanese yen is a low-yielding currency and has had an interest rate of 0.0% for a long time.
Thus, buying the high-yielding pound against the low-yielding yen brought significant swaps every day. This formed a long-term uptrend of the GBP/JPY pair that remained on the market almost till the beginning of 2008 when the Bank of England had to decrease the interest rate urgently, which was the end of carry-trading this pair.
Note that the carry trade strategy mostly suits investors and traders owning rather large deposits. For the profit from swaps to be large, you need to enter the market with quite a large position and have a decent margin of safety to be secured against possible drawdowns. For traders with rather small deposits, such trading entails increased risks due to big leverage and market volatility.
The influence of crises on swaps
As I have noted above, carry trade remains topical while the market is optimistic, and the leading stock indices grow. And when the market is struck by a crisis - as in 2008 or now, in 2020 - carry trade lists its topicality due to a swift decrease in the currency rates. Investors quit the currencies of developing economies and go to safe-haven assets.
The main safe-haven currency in the times of a crisis is the USD; its rate starts growing in the pairs with other currencies. Less safe but still protective currencies are the Swiss franc (CHF) and the Japanese yen (JPY), which also tend to strengthen in crises. Meanwhile, the high-yielding currencies of developing countries and the so-called commodity currencies (AUD, NZD, CAD) may drop seriously.
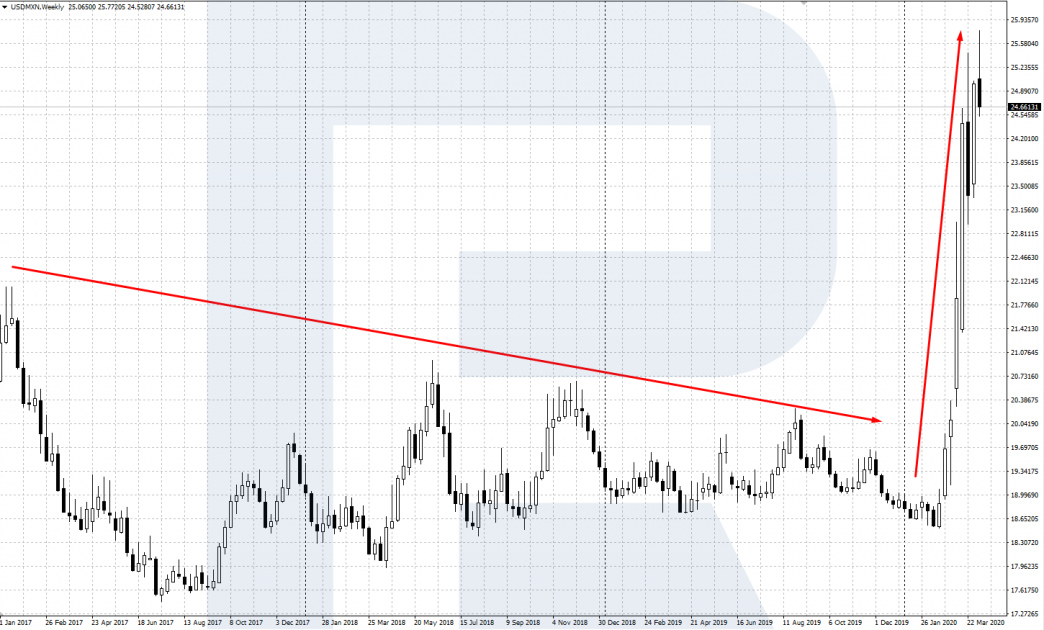
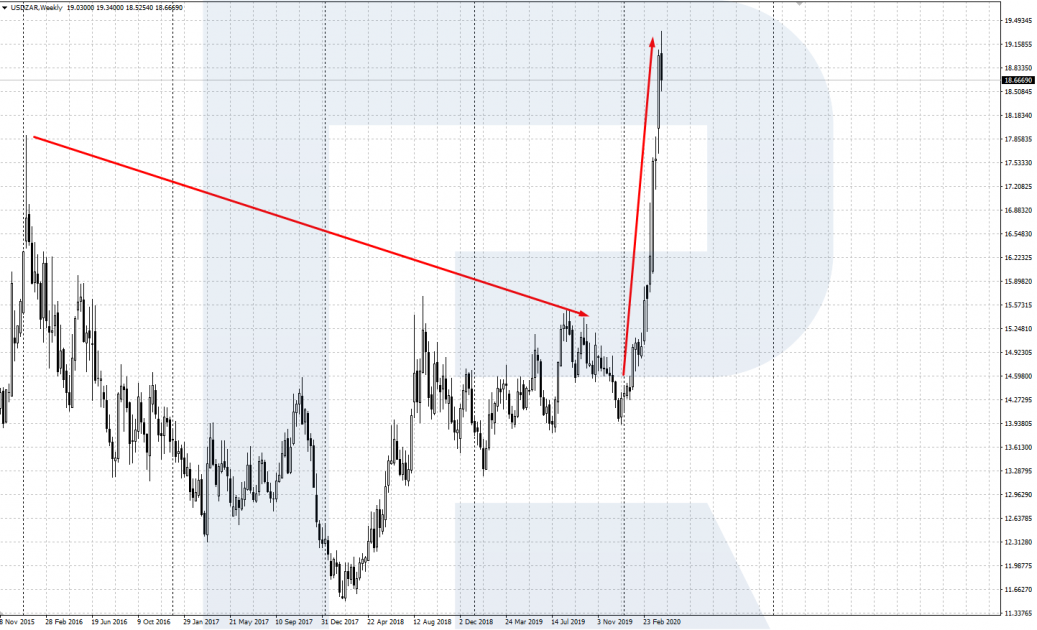
As an example, let us have a look at two high-yielding currencies: the Mexican peso (MXN) and the African rand (ZAR). They have rather high interest rates, which makes them attractive for carry-trading. Look at the charts of USD/MXN and USD/ZAR - till the beginning of the current crisis, they were trading in a limited range, and their weakness was compensated for by positive swaps.
After the current world crisis, provoked by the spread of the coronavirus, began, we can see a swift growth of the dollar on the charts. Investors started taking the capital out of weak currencies, transferring them to the dollar, which made the peso and rand fall. Even positive swaps cannot compensate for the losses provoked by such speedy falling.
Bottom line
Swaps on Forex allow making an extra profit. Such a trading strategy is called carry trade. This strategy is mostly relevant for large deposits because it requires holding a position for a long time and withstanding possible drawdowns. In the times of crisis, carry trade is better put aside as a swift decline of high-yielding currencies may entail serious losses.











