IPO of DiDi: Taxi in a Chinese Way

6 minutes for reading
Since the advent and expansion of smartphones, people of today can solve virtually any problem using different applications. When technological companies came into the private transporting business, we started forgetting the phone numbers of taxi services. Little by little, the range of services provided by such companies expanded and now includes car and scooter rental, as well as the concierge service. In many countries, there are several big taxi companies that operate using this business model. Developers of applications are constantly implementing new features based on clients' requests and feedback, thanks to which the industry has been developing exponentially for the last 5 years.

A Chinese taxi service DiDi Global (Xiaoju Kuaizhi Inc.) is planning to have an IPO at the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE). The company’s shares will start trading tomorrow, June 30th, 2021, under the DIDI ticker. This IPO is going to be one of the biggest this year. In this article, we’ll discuss how attractive this issuer is and start with analyzing its business model.
Business of DiDi Global
DiDi was founded in 2012 with a headquarters in Beijing. DiDi Global is tun by Cheng Wei, who earlier forked for Alibaba Group. In the company’s early days, he managed to persuade a small taxi company from Shanghai to connect to the application. He hired fake passengers, who commuted by taxi every day by using DiDi to make drivers believe that the application was extremely popular. Cheng owns 7% shares of the stock.
DiDi Global management continues developing services of carsharing, taxi, and bicycle/scooter rental. One of the company’s unique services is offering a car with a personal driver. In addition to that, DiDi operates in the food and cargo delivery market.
The company’s investors are Softbank Group (21.5%), a Chinese technology company (6.8%), and its American counterpart Uber Technologies (12ю8%). In 2016, Uber got its share in exchange for leaving the Chinese market. In addition to that, DiDi invested about $1 billion in Uber. But the major goal, which was to put out the competitor of business on the domestic market, was achieved, and now their rivalry continues on a more global scale.
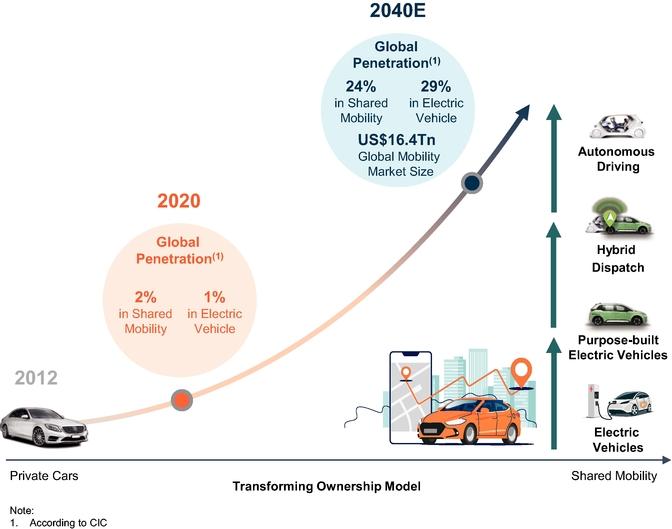
DiDi Global operates in 15 countries (almost 4,000 cities) and has 493 million active clients. DiDi processes 41 million transactions per year. In 2017, the company opened a special department responsible for the development of tactics and strategies for expanding and capturing new markets. DiDi is actively involved in developing technologies for manufacturing electric and self-driving cars, as well as Big Data (mass data processing). The latter is necessary for a more accurate forecast of demand fluctuations and city traffic.
As we can see, the company has a very effective business model. DiDi management is focused on the development of future technologies that may allow the company to grow dynamically in the next 10-15 years.
The market and competitors of DiDi Global
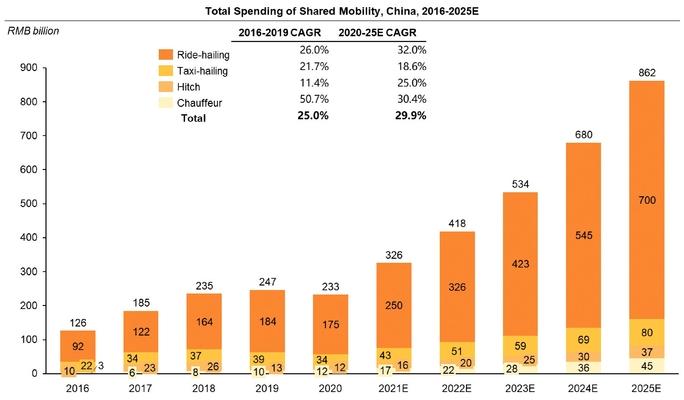
The company’s major market is China – DiDi Global is just starting its global expansion. However, one should note that the People’s Republic of China has the biggest share in the global transport market, 13.1%. As of 2020, DiDi’s target market equaled $873 billion. Before the end of 2025, the Chinese market is expected to rise up to $1.6 trillion. As a result, an average annual growth rate may be up to 18.05%.
In 2020, the global taxi, carsharing, and delivery market accounted for 8.0% of the global GDP, $6.7 trillion. This sector is quite liquid and expandы at a fast rate.
Among DiDi’s strong competitors are:
- Lyft
- Uber
- GrabTaxi
- Ola Cabs
Financial performance
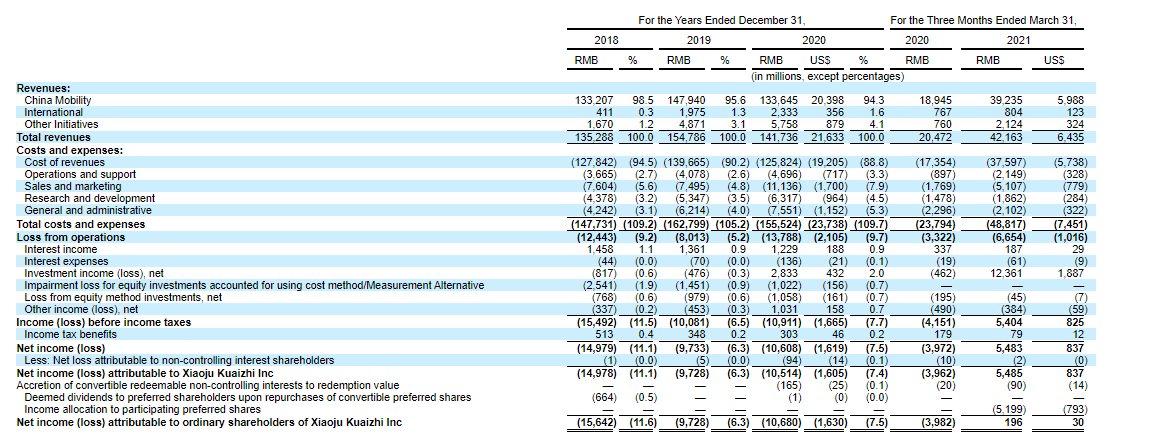
DiDi Global was a loss-making company for a long time, however, it received the net profit for the first time at the end of the 1st quarter of 2021. That’s why we’ll start analyzing DiDi’s financial performance with its revenue.
At the year-end of 2020, the company’s revenue was $21.63 billion. Due to the coronavirus pandemic, the indicator lost 8.43% if compared with 2019. However, in 2019 there was a 14.39% increase relative to 2018. At a time when the global market is recovering and many countries are removing quarantine restrictions, such a revenue growth rate would be great.
Based on the data on taxi services in China, DiDi’s market share is 2.48%. If we consider the forecast until 2025, the company’s sales might reach $41.31 billion. The indicator may be even higher because we didn’t take into account DiDi’s new business areas.
The revenue in the first quarter of 2021 was $6.44 billion with a 105% increase if compared with the same period last year. It indicates a quick recovery of the demand for the company’s services. The revenue over the last 12 months was $24.92 billion.
Cash and cash equivalents on the company’s balance sheet are $7.23 billion, while its total liabilities equal $1.7 billion. As we can see, the debt load is rather low, which means that DiDi is financially stable and has low bankruptcy risks.
Strong and weak sides of DiDi Global
Having acquired comprehensive information on the company’s business model and financial performance, let’s highlight its strong and weak sides from investors’ perspectives.
Among the advantages of DiDi, I would name the following factors:
- The company operates in a promising and rapidly-growing market.
- Sound management.
- The first net profit was received early in the year.
- The company invests in groundbreaking future technologies.
- Global expansion strategy.
- Successful competitive experience on the domestic market.
- The company’s revenue growth rate is higher than that of the market
The following might be considered as investment risks:
- There was no net profit for a long time.
- The company’s product didn’t receive recognition outside China.
- The business suffered from the coronavirus pandemic.
- Highly competitive environment.
IPO details and estimation of DiDi Global capitalization
At first, the company planned to file for an IPO in Hong Kong due to a flare-up between China and the USA. However, the situation changed after a new president Joe Biden came to power. Another advantage the NYSE has over Hong Kong is simpler and clearer listing rules. In Hong Kong, DiDi could have faced tougher compliance from regulators because it was previously fined for using unlicensed cars.
The underwriters of the IPO are J.P. Morgan Securities LLC, Morgan Stanley & Co. LLC, China Renaissance Securities (Hong Kong) Limited, and Goldman Sachs (Asia) L.L.C. During the IPO at the NYSE, DiDil is planning to sell 288 million American depositary shares (ADS) at the price of $13-14 per share. If shares are sold at the highest price in this range, the IPO may raise $3.89 billion and the company’s capitalization might be up to $70 billion.
To assess the company’s shares upside, we use a multiplier, Price-to-Sales ratio (P/S ratio). At the time of the IPO, P/S is 2.81. In comparison, the P/S of Uber and Lyft equal 9.22 and 10.09 respectively. As result, the upside for DiDi shares during the lock-up period may be over 300% ((9.22+10.09)/2.81*100%).
Considering all that said, I’d recommend this company for mid/long-term investments.