Foreign Currency Trading 2024: What to Expect

9 minutes for reading
On 8 February 2024, we examined how the exchange rates of the leading world currencies had changed in 2023 and discussed the key factors that will impact their performance in 2024. Additionally, we shared short and medium-term expert forecasts for the major currency pairs.
You can visit the RoboForex Market Analysis webpage for the latest forex forecasts.
The strongest and weakest currencies in 2023
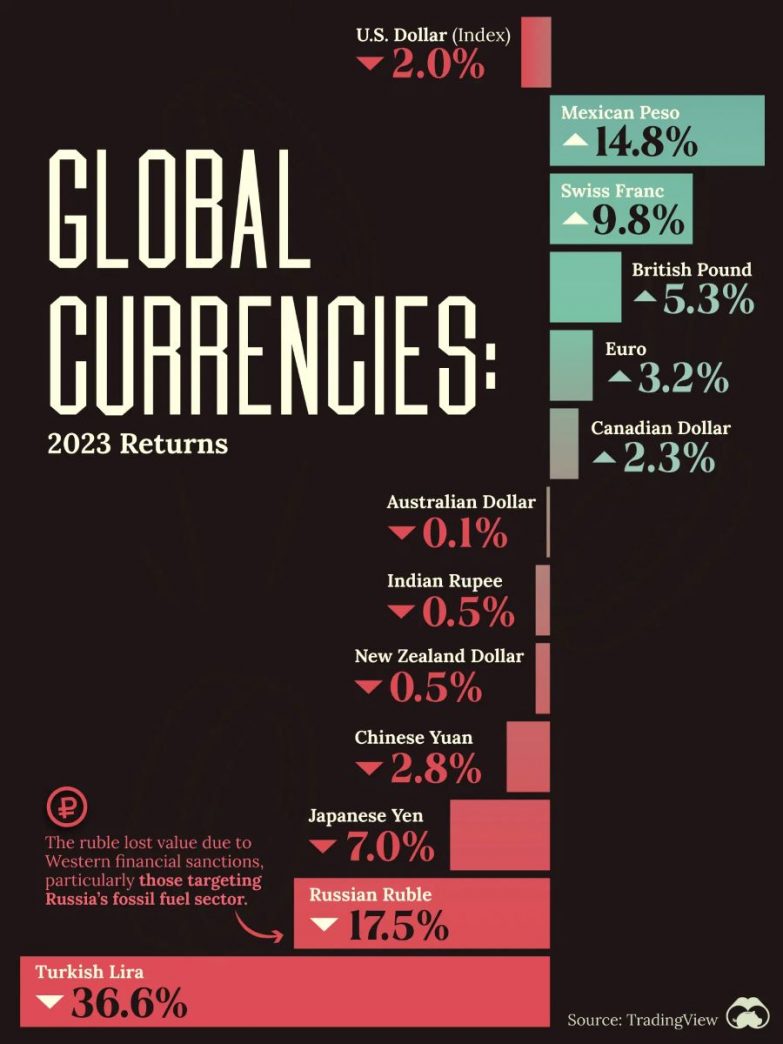
In 2023, many central banks were actively fighting inflation, resulting in relatively high volatility in the currency market. According to Visual Capitalist, the Mexican peso (MXN) saw an impressive increase last year, appreciating 14.8% against the US dollar (USD). This development occurred amid aggressive interest rate hikes by Mexico’s central bank. When writing, the interest rate was 11.25%.
The Swiss franc (CHF) also demonstrated steady growth of 9.8% due to geopolitical turbulence. The British pound (GBP), Canadian dollar (CAD), and euro (EUR) strengthened moderately within the range of 2-5% by year-end due to the interest rate hike policy pursued by the central banks.
The Australian dollar (AUD), New Zealand dollar (NZD), and Indian rupee (INR) ended the year with little to no changes, declining slightly by −0.1%, −0.5%, and −0.5%, respectively. The Chinese yuan (CNY) slid moderately by 2.8% in 2023.
The worst-performing currencies of the year were the Japanese yen (JPY), Russian ruble (RUB), and Turkish lira (TRY), which dropped by 7%, 17.5%, and 36.6%, respectively. The low-rate policy influenced the yen; the ruble is under pressure from the sanctions imposed following the onset of full-fledged war in Ukraine, and the lira is struggling due to domestic political and economic challenges.
The US Dollar Index (DXY), showing changes in the US currency value against a basket of the world’s major currencies, ended 2023 with a 2.0% decline.
Key factors influencing currencies in 2024
Inflation and central bank policy
The critical factor affecting exchange rates over the last two years was multiple central banks' aggressive interest rate hike cycles to combat inflation. The US regulator initiated these actions in Q1 2022, with the indicator increasing to 5.5% in less than two years.
Most of the world’s developed countries experienced monetary policy tightening to a similar extent. The Bank of England began to raise the interest rate at the end of 2021, a couple of months before the Federal Reserve, with the rate in the UK reaching 5.25% following 14 consecutive hikes. The European Central Bank began to increase the interest rate in mid-2022, pushing it up to 4.5%.
The central banks of Australia, Canada, and other countries followed suit, while the Bank of Japan was practically the only one among the most prominent regulators to pursue an adaptive zero-interest rate policy. This approach dominated the world for the first two years after the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic.
In 2024, currencies could be greatly impacted by a reversal of the above monetary policy trends. Inflation in the world and individual countries has been steadily falling over the last six months, gradually approaching the target levels set by the central banks. According to recent comments from the Federal Reserve, Bank of England, and ECB officials, it can be presumed that rates have probably reached their peak values in this cycle.
They will likely remain at the achieved levels for a while, potentially decreasing gradually later as part of the monetary policy normalisation cycle, provided that inflation steadily slows down. Since the Fed has already hinted at this, experts forecast the first rate cut as early as March 2024. The interest rate reduction will pressure the exchange rates of national currencies.
US elections
Historically, the US dollar exchange rate tends to rise under Democratic presidents and decline under Republicans. Therefore, the currency market becomes especially volatile in the face of uncertainty surrounding upcoming presidential elections in the US, as stated by Business Insider analysts. This event will determine not only the US policy but also the US dollar exchange rate against other currencies.
Donald Trump is expected to become the leading nominee from the Republican party, having won the primaries in the coming months. He will face incumbent Democratic President Joe Biden in a tightly contested election. Their rematch, accompanied by heated rhetoric and the potential for social conflict, may affect investor sentiment and currency markets. Trump is committed to higher tariffs, which will push up inflation and increase the US dollar exchange rate, putting the Chinese yuan, euro, and Mexican peso under pressure.
According to Universal Partners, JPMorgan analysts expect the 2024 US presidential election to boost the dollar’s status, driven by the prospect of a trade war. Bank of America suggests that the election may significantly affect the exchange rate of the Japanese currency, as Democratic presidents contribute to the yen’s weakening against the US dollar, while Republican administrations tend to strengthen it.
Trends in the global economy
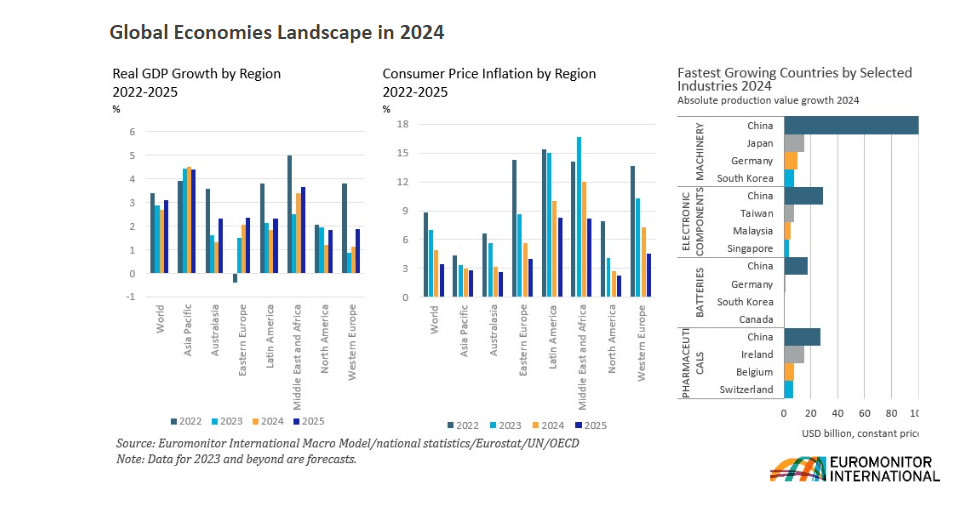
The International Monetary Fund projects that global economic growth will remain at 3.1% in 2024 and rise to 3.2% in 2025. Higher rates and a withdrawal of fiscal support amid high debt exert pressure on economic activity.
In most regions, the inflation rate is slowing down faster than expected amid unwinding supply-related issues and restrictive monetary policy. Global inflation is projected to fall to 5.8% in 2024 and 4.4% in 2025, with the outlook for the next year being revised downwards.
According to the Euromonitor International survey, the global economy in 2024 will see a further slowdown in real GDP growth, with the forecast set at 2.7%. Higher interest rates and depleting savings will lead to a slowdown in consumer spending and lower business investments.
Geopolitical risks
- Russian-Ukrainian war: Military actions continue to pose a significant geopolitical risk in 2024. The full-scale war has triggered a humanitarian crisis and increased risks in global capital flows, trade, and commodity markets worldwide. Russia's invasion of Ukraine has made relations between NATO and Russia highly unstable. Since neither side appears capable of achieving a convincing victory shortly, and a ceasefire or conflict resolution seems unlikely, the expected course of events will persist. The likelihood of direct global military conflict between Russia and NATO is currently assessed as low, but it still exists. If this scenario unfolds, the consequences will be dire for the entire world.
- US-China standoff: Despite multifaceted relations between these countries, especially in trade, supply chains, and the economy, recent years have increased communication complexity. China and the US seek to implement policies of responsible competition, but there's a risk of worsening relations. There are areas of shared interests and contradictions between the countries. China has threatened to sell US treasury bonds, prompting the US to blacklist some Chinese technology companies. Concerns are growing about the potential escalation of trade tensions between the countries into a financial rift. Such a conflict could lead to severe disruptions in global financial markets.
- Middle East conflict: Events in this region are a source of significant uncertainty and create the risk of further indirect or direct confrontation between global powers. If the conflict between Israel and the Gaza Strip escalates into a full-scale war, there could be broader intervention by Gulf states, as well as Iran and the US. Escalating conflict with the involvement of new participants could trigger a humanitarian crisis and immense disruptions to global energy prices and supply chains, which, in turn, would impact the entire global economy and financial markets.
- Cyber threats: Cyberattacks represent a geopolitical risk that is becoming increasingly widespread. The digitisation of critical national infrastructure means that various vital structures, such as power grids, water supply, and transportation systems, are increasingly vulnerable to potential cyberattacks. Successfully targeting any of these systems could have serious consequences, including loss of human lives and economic damage.
International cooperation in effectively combating cyberattacks is complex, especially considering the problematic relations between many countries. With increasing geopolitical tensions between the US, China, and Russia, the likelihood of large-scale cyberattacks as a tool of state confrontation is growing.
Expert forecasts for 2024
EUR/USD
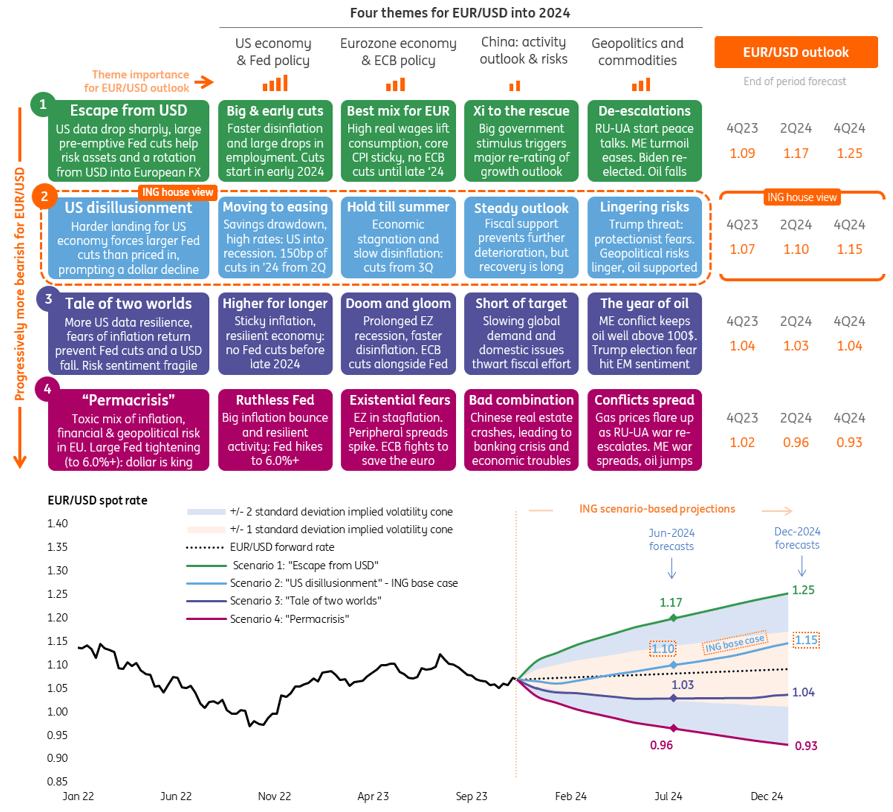
The base 2024 forecast from ING Group economists suggests that the US dollar will follow a bearish trend during the year. Specialists expect economic growth to be a mere 0.5%, and the Federal Reserve will slash the interest rate by 150 basis points already this year, starting from the second quarter. The quotes of the EUR/USD pair, which serves as a reference point for the currency market in general, are projected to hover within a wide range of 0.88-1.21. Possible scenarios of fluctuations in the pair’s exchange rate are outlined below:
GBP/USD
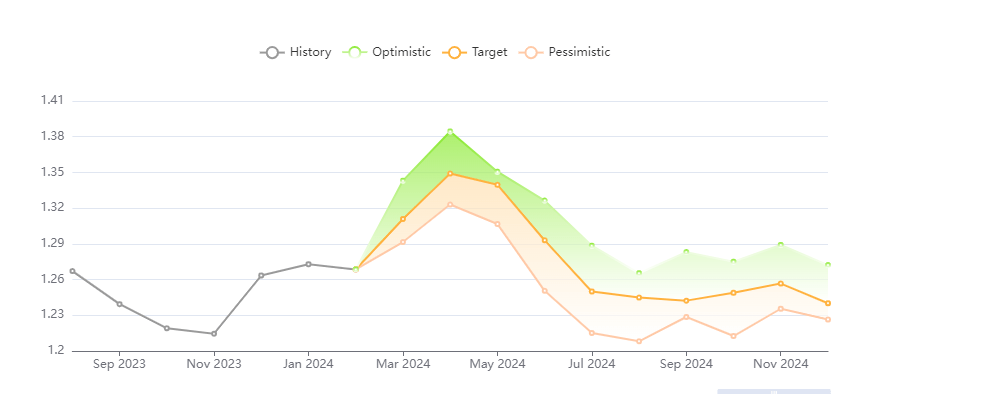
Forecasts for the GBP/USD exchange rate fluctuations in 2024 from the Panda Forecast analytical portal include three scenarios: optimistic, pessimistic, and the weighted average target level. All three scenarios are set forth below.
USD/JPY
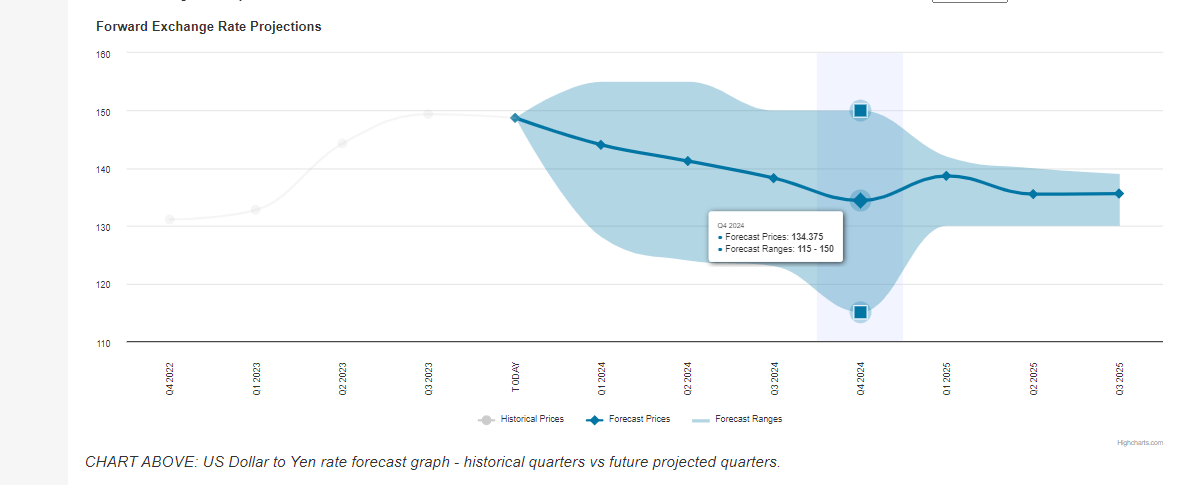
Specialists of the exchangerates.org.uk analytical resource expect the USD/JPY quotes to remain within a wide range of 115.00-155.00 in 2024. The exchange rate is projected to fall to 144.04 by the end of the first quarter and 134.37 by the end of the year.
Conclusion
The US Federal Reserve and other central banks are expected to change their monetary policies from tightening to normalisation in 2024. The currency market will be significantly affected by factors such as expectations of interest rate cuts by most prominent central banks, potential slowdown in the global economy’s growth rates, US presidential elections, and geopolitical risks. Experts forecast that the US regulator will be the first to begin slashing the interest rate, which might place the US dollar under pressure against other leading world currencies.