How Economic Recession Influences Investors' Behaviour
6 minutes for reading
This overview describes what economic recession is and why it happens. We will analyse a case of global economic recession and see some advice concerning how to behave during a crisis.
What is economic recession
Recession is a serious and lengthy decline of economic activity, characterised by a decrease in production and employment that results in falling of income and spending of households. This phenomenon may last over several months and is usually followed by a decline of the GDP.
Experts from the US National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) have given their own definition. They state that recession is a significant economic decline that starts at the high of preceding growth and ends at the low of subsequent falling.
The decline of economic activity must be quite deep and lengthy to have the right to be called recession. It may last just several months but it will take the economy years to get back to the previous peak.
Reasons for and signs of economic recession
Multiple economic theories struggle to explain why and how economy escapes a lengthy uptrend and starts falling. For example, abrupt and stable growth of oil prices due to a geopolitical crisis may lead to growth of spending at the global market and provoke a global economic recession.
According to the conclusion made by the US Congress Special Commission, the economic recession 2008-2009 was provoked by such factors as mistakes in financial regulations and in corporate management, excessively high debts of households, wide use of high-risk derivatives, and growth of non-regulated shadow banking.
Spread of COVID-19 in 2020 and quarantine restrictions are yet another example of an economic shock that can provoke recession. It might be just speeding up the process that could be inevitable due to other factors.
Analysts single out two main signs of an approaching economic decline:
- Gradual decline of the country's GDP during two quarters in a row.
- Inverted curve of bond yield. Normally, long-term bonds show better yield than short-term ones. However, in such circumstances yield of short-term bonds exceed that of long-term ones.
What is recessionary gap
Recessionary gap is a gap between the quantity of goods and services produced during full employment and in recession. In other words, this is the difference between factual and potential production statistics of the country's economy, where the factual results are worse than potential ones.
This gap is an indicator by which economists measure the lost potential of the economy that works in recession. They measure what the economy could produce if it worked full power and they detract what it really produces to see the deficit.
How US recession 2008 influenced global capital markets
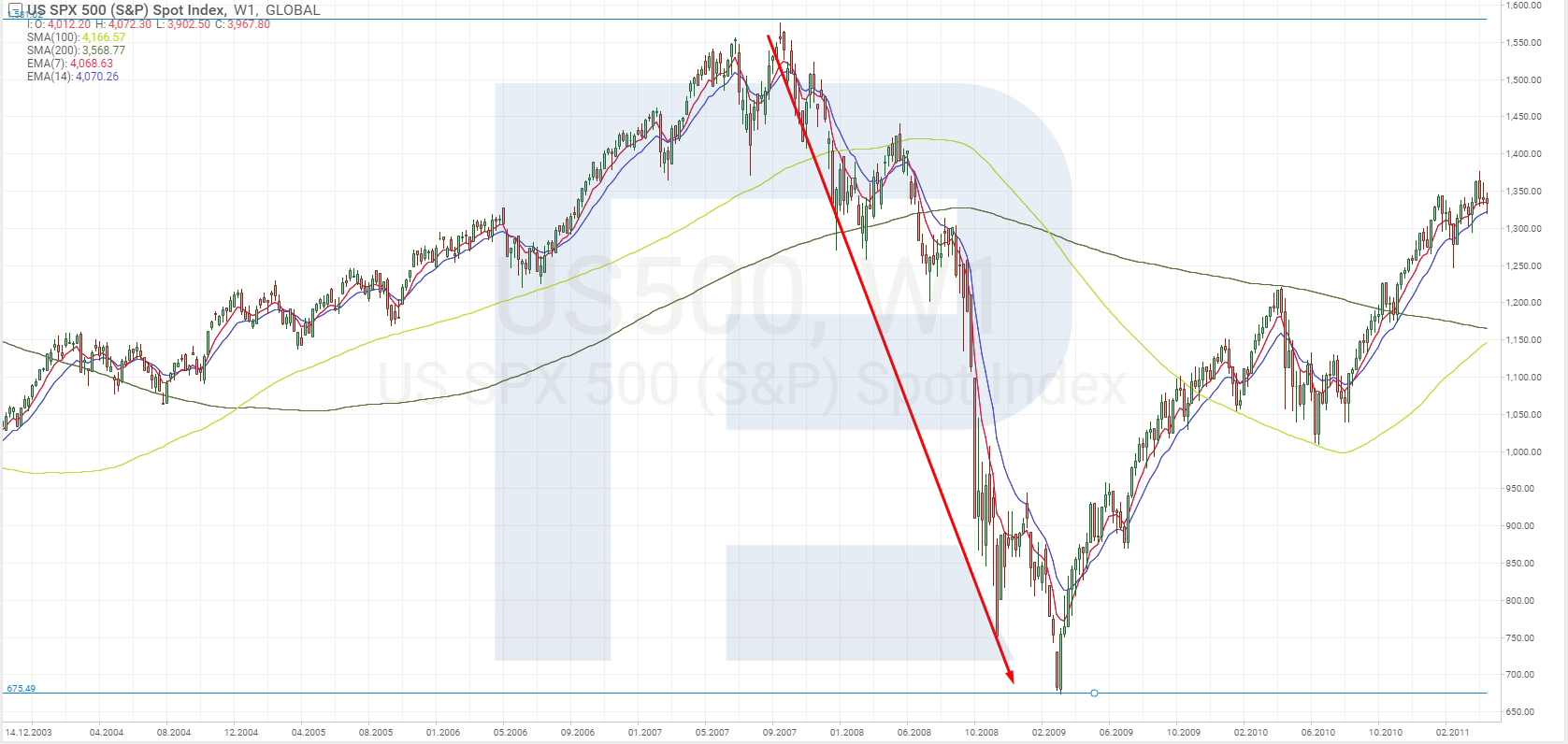
The economic recession and crisis in 2008 followed a lengthy time of growth of housing prices and a boom of mortgaging in the US. The overall economic peak happened in December 2007,and the NBER considers this month the beginning of the recession. At the start, the decline of the economic activity was modest but sped up abruptly in autumn 2008 when stress in financial markets reached the top. The US GDP dropped from +2% to -2.6%, and the unemployment rate grew from 5% to 10%.
January 2007 through September 2009 large US and European banks lost more than $1 trillion on toxic assets and unsecured loans. A lack of confidence of investors in the paying ability of banks alongside loans becoming less affordable led to an abrupt decline of prices for goods and services. The crisis quickly turned into a global economic shock, making several large banks go bankrupt. Economy worldwide slowed down because crediting became tough and global trade went feeble.
This recession in the US became the longest one since World War 2 and lasted 18 months. The S&P 500 index started falling at the end of 2007 and, having lost more than 50%, began recovery only in the middle of 2009.
Global economic recession 2022
These days, the global economy is slowing down abruptly. War in Ukraine, growth of prices for energy carriers and foods alongside imbalance between the demand for them and supply provoke growth of global inflation. According to forecasts of analysts, a decline of the buying ability of households and toughening of the credit and monetary policy will bring down the growth of the US economy up to 2.3% this year and up to 1% in the next year.
In China, the slow-down of economic development turned out stronger than expected due to COVID-19 breakouts and imposed quarantine measures. In the Euro zone, growth dropped to 2.6% this year and will reach 1.2% next year. According to the forecasts of the IMF, inflation and the geopolitical crisis have already put the global economy on the verge of recession.
Economic recession vs depression
As was mentioned above, economic recession is a temporary decrease in business activity characterised by a decline of production and employment.
Depression is a deeper and longer stress for the economy. It is characterised by an abrupt falling of industrial production, high unemployment rates, a serious decline or a total halt in building, and a serious decline of international trade and money flows.
In other words, a depression is an especially deep and long recession though no formula describing it has been invented yet. A bright example is the Great Depression of the 1930s that brought production in the US down by 33%, stocks — by 80%, while the unemployment rate hit 25%.
What to do during economic recession
It should be realised that economic declines happen, so we need to be prepared. One should nor panic neither make hasty decisions. The crisis is temporary, and it calls for investors to be cautious and look for new perspectives.
Here is some advice from financial counselors on how an investor should behave during recession.
- Accumulate free cash not to kiss investment opportunities, such as buying assets at mouthwatering prices or entering securities at the very bottom. The money should be kept on deposits from were you can withdraw it without losing interest or in short-term treasury or corporate bonds of most reliable issuers.
- Build up financial reserves. It would be best to have a reserve that equals your annual spending. For businesses this means keeping the current assets to current liabilities ratio above 1.
- Repay expensive loans early. Debt payments should not take up more than 30% of monthly income. This allows decreasing risks of loan arrears and non-payments.
- Prefer short-term bonds for investing. Before a recession starts, the number of short-term bonds of reliable issuers in the portfolio should be increased. Meanwhile, positions in stocks should mostly be closed, except for the stocks of several protective branches with good dividends.
Closing thoughts
Recession is a crisis phenomenon followed by a serious decline in the country's economy. Stock markets usually fall abruptly during several months. At such times, investors must be very cautious, avoiding risks in safe-haven assets to protect their capital.
However, such crises open new opportunities because a decline is normally followed by a lengthy recovery and growth of the economy and stock markets.







