Coursera IPO: a University on Your Couch

7 minutes for reading
After getting their main education, a lot of people may realize that their hearts aren't in it or that a degree they got doesn’t lead to a substantial salary and a decent standard of living. If such situations occurred in the past, people had to get an alternative higher-education degree, apply for retraining courses, or acquire new skills by means of self-learning.
With the development of the Internet, there appeared a great variety of educational resources and first-ever online courses. However, the opportunity to get real high school knowledge came within reach only after the appearance of educational platforms and Coursera became one of the leading companies in this area.

On March 5th, 2021, COURSERA, INC. filed an S-1 IPO form at the NYSE to the SEC. Let’s get to know the company’s business model, financial performance, and competitive advantages better. At the end of our article, all these aspects taken together will help us to decide whether the company’s shares are worth investing in.
COURSERA business
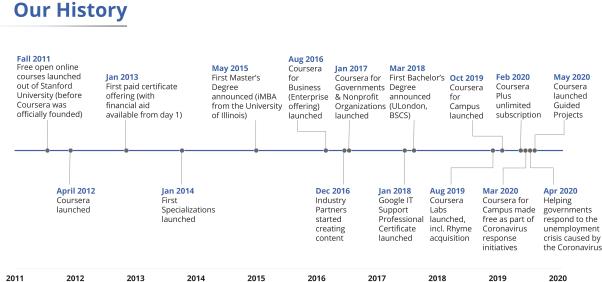
COURSERA was founded in 2012 by two Stanford University computer science professors Daphne Koller and Andrew Ng. The company’s CEO is Jeff Maggioncalda, who is already experienced in taking a company public – in 2018, he took part in the IPO of Financial Engines. Coursera’s major investors were such venture funds as NEA, Future Fund, GSV Capital, and Kleiner Perkins. The company’s history can be found below.
Coursera is one of the world’s best online course providers. Users register for the courses they are interested in and take them on the company’s website or application. Teaching methods are most closely resembling university programs. Upon completing the course, students get certificates confirmed by the corresponding universities.
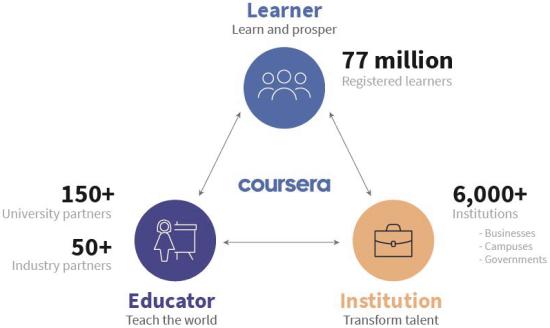
As of the year-end of 2020, more than 150 universities offered upwards of 4,000 specialty courses through Coursera. Students could get a degree in over 25 specialties much cheaper if compared with a full-time mode of study. A master’s or bachelor’s degree can be received through the platform for $9,000-45,000.
As of the reporting date, December 31st, 2020, Coursera had 77 million students.
The company ranks 4th in the Disruptor 50 CNBC rating, which includes private businesses that significantly influence market competition. Another Coursera’s branch is advanced training courses from leading transnational companies, such as Google, Microsoft, Amazon, IBM, and others. Such certificates of attendance may help graduates to get an edge when applying for a job at the above-mentioned companies. The coronavirus pandemic started in 2020 boosted the business of Coursera.
The market and competitors of COURSERA
According to HolonIQ, the global educational market was $2.2 trillion in 2019, $36 billion of which were made by online learning. Since we’re in the process of the global technical-and-economic model transformation, people’s needs for new and improved skills will nothing but increase. That’s why HolonIQ believes that the online learning market will reach $74 billion by 2025. As a result, the average annual growth rate will be more than 20%.
It will allow companies of this sphere to demonstrate an annual growth rate of over 50%, thus making them pretty attractive for both aggressive and conservative investors.
Coursera’s principal competitors are Udemy and Fiverr Learn. When it comes to Fiverr, this platform is the least “dangerous” for Coursera because it offers only 29 online courses in digital marketing and creative ideas. The platform positions itself as a resource for freelancers or those who look for secondary work and does not offer any opportunities to get a degree or a university certificate. Fiverr Learn is not a public company yet but remains a pretty popular platform in its niche.
Udemy is a more serious competitor for Coursera as it offers more than 100,000 different courses, which include both academic courses and materials for pursuing proper and unusual hobbies. The quality of the platform courses is quite high but they are not authorized by universities, that’s why Udemy can’t offer students any certificates and degrees.
Financial performance
At the moment of filing for an IPO, Coursera Inc. wasn’t generating any net profit, so let’s start analyzing the company’s financial performance with its revenue because it best reflects the growth rate of the company’s business and market share.
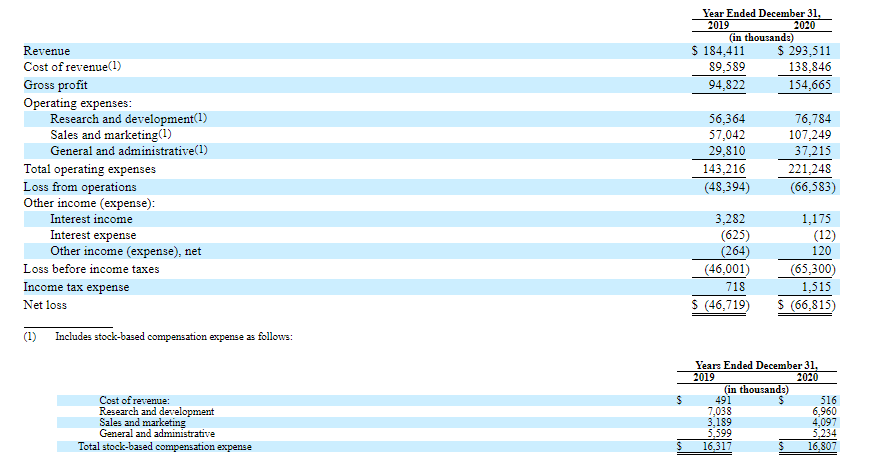
As of December 31st, 2020, the company’s revenue was $293.51 million, which is a 59% increase if compared with 2019. Also, the detailed report shows that the biggest growth rate was recorded in the second quarter of 2020.
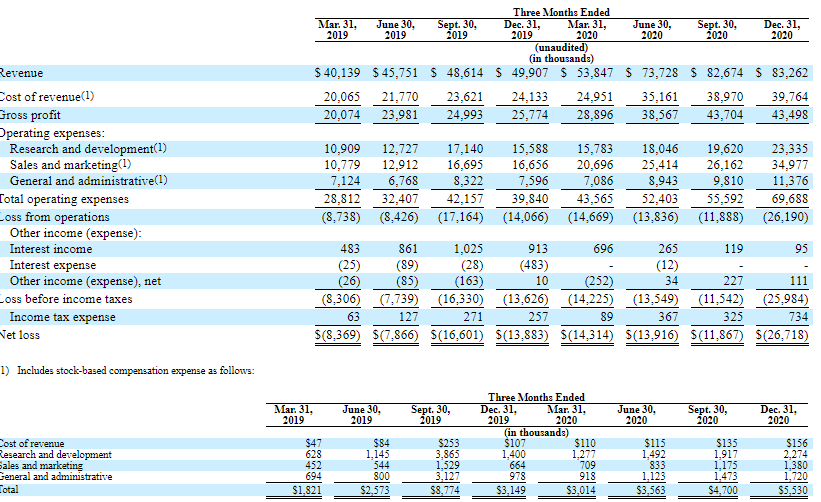
As we can see, the indicator improved from $53.85 to $73.73 million in April-June. The relative growth was 36.92%, although an average quarterly growth is usually 9-11%.
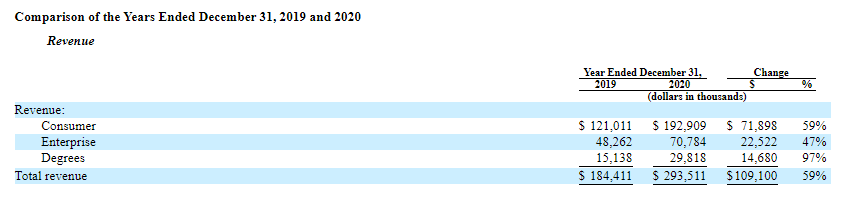
The biggest surge in the interest of the platform users was caused by the opportunity to get a degree as the number of recipients increased by 97% over a year. As of December 31st, 2020, cash and cash equivalents on the company’s balance sheet were $79.88 million, while the net loss in 2020 was $66.82 million. However, a positive factor here is the cost of revenue, which went from $89.59 to $138.85 million, a 54% increase from 2019 to 2020.
We should also note that the COVID-19 pandemic effect turned out to be extremely positive for revenue growth. However, even without it, the growth rate was worthy of a wise investor’s attention. The cost of revenue growth gives reasons to expect the net profit in the nearest future.
Strong and weak sides of COURSERA
Taking into account everything abovementioned, we can evaluate all pros and contras of Coursera Inc. The company’s undeniable advantages are:
- The high growth rate of the revenue by 59% every year.
- Coursera operates on the “booming” market of online education, which may reach $74 billion by 2025.
- The company’s business got stronger during the coronavirus pandemic.
- Coursera cooperates with the leading companies from S&P 500 and Nasdaq 100.
- The company collaborates with us universities and government institutions from 300 countries.
- Coursera ranks 4th in the Disruptor 50 CNBC rating.
Risk factors of investing in Coursera in my opinion are the following:
- Dependence on cooperation with universities and government institutions.
- A strong competitor represented by Udemy.
- The company is loss-making and doesn’t pay dividends.
- The company management avoided predicting how its revenue may change after the COVID-19 pandemic is over.
IPO details and estimation of COURSERA capitalization
During several rounds of financing, Coursera raised $443.1 million. The underwriters of the IPO are Loop Capital Markets LLC, William Blair & Company, L.L.C., Telsey Advisory Group LLC, Needham & Company, LLC, Citigroup Global Markets Inc., UBS Securities LLC, KeyBanc Capital Markets Inc., Raymond James and Associates, Inc., Stifel, Nicolaus & Company, Incorporated, Truist Securities, Inc., William Blair & Company, L.L.C., D.A. Davidson & Co., Goldman Sachs & Co. LLC, and Morgan Stanley & Co. LLC.
The proposed maximum aggregate is standard, $100 million. The IPO date unknown yet and will be defined by underwriters. To assess the company’s capitalization, we use the Price-to-Sales ratio (P/S Ratio), because similar companies are not public and Coursera doesn’t generate a net profit. For tech companies, the average value of the ratio is 10. In this case, the company’s capitalization may be up to $2.94 billion ($293.51 billion*10).
Thanks to several competitive advantages, strong financial performance, and the “booming” market, we may recommend adding Coursera shares to mid/long-term investment portfolios.