Unemployment Rate, and How to Use It in Forex

6 minutes for reading
As a rule, trading in financial markets is based on tech analysis, expert advisors, and various indicators. Attempts to make a profit on the publication of some important economic news and its analysis stands a bit aside.
One of the strongest indices that can move the market is Non-Farm Payrolls; this index shows the number of workplaces out of the farming sector in the USA. As long as the US dollar is the world’s leading currency, the state of the US economy worries investors and traders, naturally.
Some short time ago, there was a separate category of active traders that were looking forward to the publication of this index because, after the publication, the market could cover hundreds of points in one direction in just a couple of minutes, which was a good opportunity for making a profit. The rest of the week such traders enjoyed themselves, waiting for Friday and NFP.
The unemployment rate: what is it and how does it influence the market?
We may say that employment is the basis of any economy. If workplaces are abundant, more goods get to the market, and the employees get a higher wage. They further spend their revenue on other goods and services, thus increasing demand. However, some say that extremely high or low employment rates might both be harmful to the economy.
If the unemployment rate is high, social tension increases, the share of the middle class shrinks, and so does the real income of the population. If the unemployment rate is too low, employees may lose motivation for working and making high-quality products: there are almost no rivals, seeking the same workplace, hence, no stimulus to become the best. The interests of the employer and the ultimate consumer, who gets a product of mediocre quality, also suffer.
The optimal unemployment rate should be within 3-7% of a country’s working population. Of course, the optimal level might differ from country to country, and the same unemployment rates in two countries are hardly comparable. Anyway, significant fluctuation from the average level may provoke a market movement, which traders will try to use for making a profit.
What does a trader do before the publication of unemployment rate data?
A trader always has a choice, and if the market looks too unclear, lacking quality signals, better stay away from it.
In our case, we may choose out of the following patterns:
1. Stay out of the market.
News always brings some risk, and we do not know how the price might react. It is up to you to decide whether to assume additional risks or calm trading without news suits you better.
2. Place the Stop Loss to the breakeven
If you have some open positions, try moving the Stop Loss to the breakeven, indulging in a chance to make even more money. You might have opened your trade by the trend, and the news will simply push the price forward – in this case, you will make even more money. Moreover, you must let your profit grow – and the publication of the unemployment rate data is one of the chances to get maximum profit from your trade.
3. Close all positions
Close, wait, and see how the market reacts upon the news. You might already have some profit and have no desire to risk it, thus you conservatively decide to get what you have and watch the situation with no open positions at hand
4. Ignore the news
This is your option if you trade by a strict system that takes no account of economic indices. For example, if we trade by the crossing of the Moving Averages, we do not care about what is going on in the market and what news is to be published soon. Moreover, it might happen so that the market goes in the direction of our signal at the publication of the news.
5. Try to make a profit on the news
For this, we use pending orders – this is one of the easiest ways to make money on the news without analyzing the current market situation.
Here, you must realize that even if you decide to make a profit on the news, your attempt will still be just an attempt.
Most often, traders place pending orders 20-30 points away from the current price. At the moment of the publication, if something goes unexpectedly, the market may fluctuate significantly in either direction, triggering one of the orders. The worst thing that might happen is the triggering of both orders, which will give us a loss of 40-60 points (the width of our channel).
Examples of market reaction to the unemployment rate indices
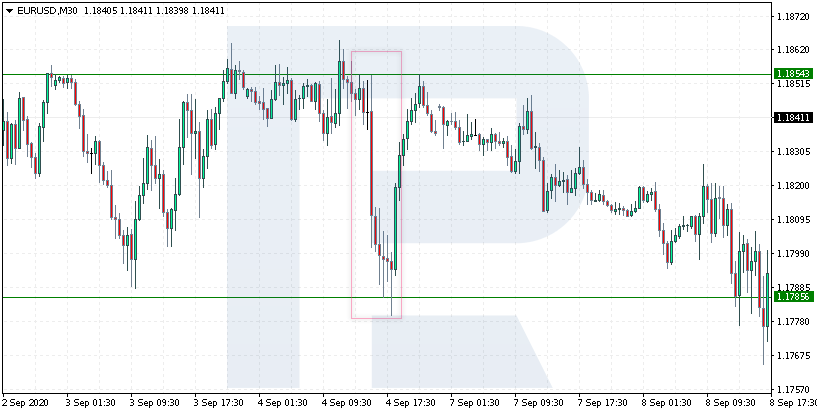
Let us have a look at several market reactions to the publication of Non-Farm Payrolls. On September 4th, 2020, at the publication of the index, the EUR/USD price dropped from 1.1854 to 1.1785 (69 points). However, after testing the support level, the price pushed off it and went back up – this might be because of a strong uptrend in the pair.
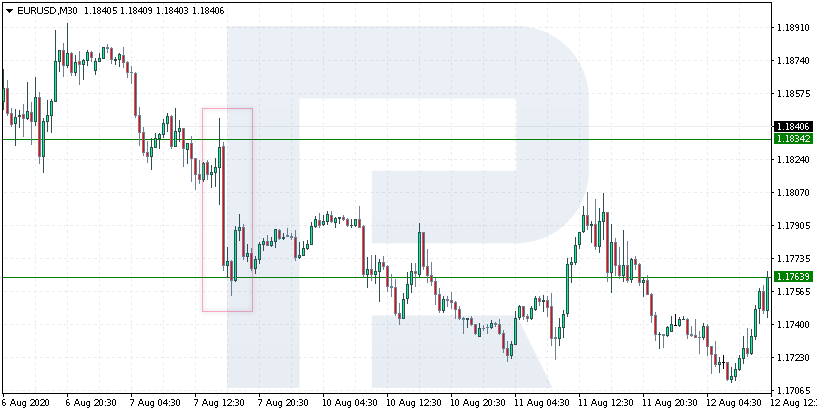
Next example: on August 7th, 2020, the price again demonstrated a drop from 1.1834 to 1.1763 (71 points). Here, the price bounced off the resistance level and reached a new low. Then the decline continued.
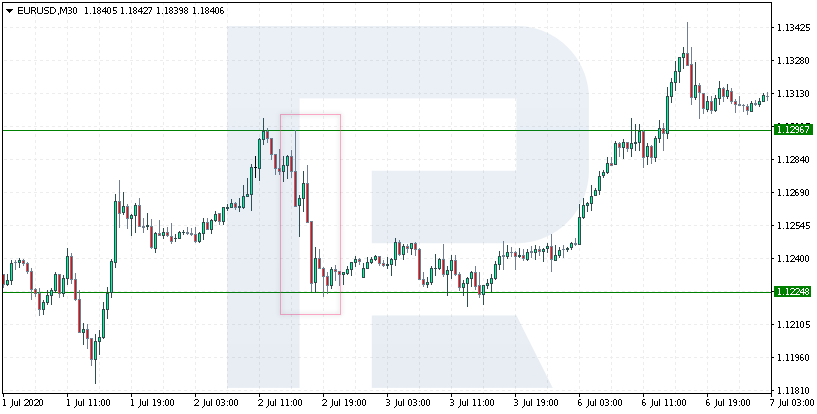
And one more – July 2nd, 2020. The price fell from 1.1296 to 1.1224, i.e. by 72 points. Here again, it dropped from the resistance to the nearest support level. Nonetheless, the market went upwards.
As we see, in those cases, the publication of the news helped the dollar become stronger against the euro but none of the three pieces of news reversed the market or made the trend change.
Closing thoughts
The publication of the unemployment rate data may noticeably increase market volatility. Many traders call Non-Farm Payrolls an index that moves markets, however, it cannot reverse the current trend.
In the examples above, we do see that the market reacts to this data; in rare cases, investors ignore the index, and no strong movements can be noticed. Any trader can stud the history of market behavior at the publication of the news and try to find certain laws that will later help make money on the news.
On the other hand, the trader may stay away from the market because there is a risk that the market will go against their position. It is up to everyone to decide.







